Argumentative essays are among the most structurally demanding forms of academic writing. They require students not only to take a position on a debatable issue, but also to organise ideas in a way that demonstrates logic, balance, and critical judgment. For many students, the challenge is not understanding the topic, but knowing how to structure the argument so that it is convincing to an academic reader.
University markers evaluate argumentative essays as much by their structure as by their content. A poorly organised argument, even when supported by good research, often appears weak or underdeveloped. Conversely, a clearly structured essay allows the reader to follow the reasoning step by step, which strengthens credibility and coherence.
This article explains argumentative essay structure in detail, clarifying how each section functions, how ideas should progress, and how students can meet formal academic expectations across disciplines.
What Is Meant by Argumentative Essay Structure
Argumentative essay structure refers to the organised framework that guides how an argument is presented from introduction to final synthesis. It determines the order in which claims, evidence, counterarguments, and conclusions appear.
Unlike narrative or descriptive writing, argumentative essays follow a logic-driven structure. Each section must serve a specific purpose in developing and defending the central position.
This structure ensures that persuasion occurs through reasoning rather than assertion.
Examiner expectation: A strong argumentative essay demonstrates logical progression, not just strong opinions.
The Role of Structure in Academic Argumentation
Structure is fundamental to academic argumentation because it reflects disciplined thinking. An argument that is clearly organised signals to the reader that the writer understands both the issue and the academic conventions governing debate.
In higher education, structure also functions as a form of transparency. It allows markers to assess whether claims are supported, counterarguments are considered, and conclusions are justified.
Without a clear structure, even accurate content can appear incoherent or unconvincing.
Core Components of an Argumentative Essay
Although variations exist across disciplines, most argumentative essays share a core structural framework. Each component contributes to the overall strength of the argument.
Understanding these components helps students plan their essays more effectively.
- An introduction that frames the debate and presents the position
- Body paragraphs that develop and support the argument
- Consideration of counterarguments
- A closing section that synthesises the reasoning
These components must be connected logically rather than treated as isolated parts.
Structuring the Argumentative Essay Introduction
The introduction establishes the academic context of the argument. It introduces the topic, explains why it is significant, and narrows the focus toward the specific debate being addressed.
A strong introduction moves from general background to a clearly defined thesis statement. This thesis communicates the writer’s position and sets expectations for the argument that follows.
Introductions should avoid excessive detail, reserving full argument development for later sections.
The Thesis Statement as Structural Anchor
The thesis statement is the structural anchor of the entire essay. It defines the position being defended and determines how the body paragraphs are organised.
An effective thesis is specific, debatable, and supported throughout the essay. Vague or factual statements do not function as argumentative theses.
All subsequent sections should clearly relate back to this central claim.
Organising Body Paragraphs for Logical Progression
Body paragraphs form the core of the argumentative essay structure. Each paragraph should advance one clear reason that supports the thesis.
Academic readers expect paragraphs to follow a logical internal structure, often beginning with a topic sentence that signals the argument being made.
The remainder of the paragraph should explain, support, and analyse that claim.
Internal Structure of an Argumentative Body Paragraph
Well-structured body paragraphs typically follow a consistent pattern. This ensures clarity and coherence.
- Introduce the claim or reason
- Explain its relevance to the thesis
- Present supporting evidence
- Analyse the evidence critically
- Link back to the main argument
This pattern prevents paragraphs from becoming descriptive or disconnected.
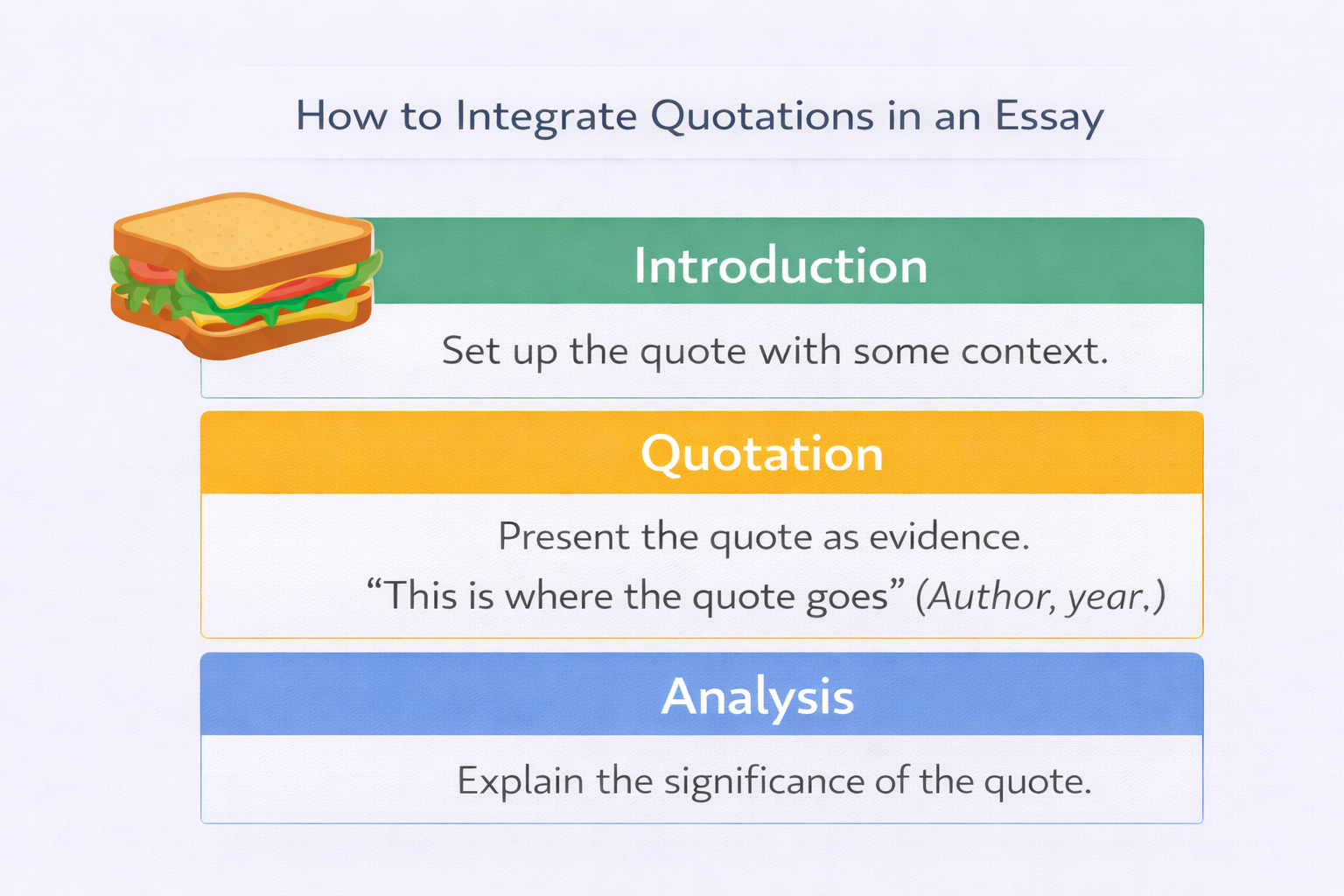
Using Evidence Within the Essay Structure
Evidence must be integrated into the essay structure rather than inserted as isolated quotations. Its placement and explanation are crucial.
In argumentative essays, evidence supports specific claims rather than standing alone. Each piece of evidence should directly strengthen the argument being made.
Analysis is essential; without it, evidence does not persuade.
Balancing Multiple Supporting Arguments
Argumentative essays often require multiple supporting points. These should be arranged strategically, usually from strongest to weakest or from foundational to more complex.
The order of arguments influences persuasiveness. A poorly sequenced essay can confuse readers or weaken the overall case.
Transitions between paragraphs help maintain continuity and flow.
Where Counterarguments Fit in the Structure
Counterarguments are a defining feature of strong argumentative essays. Structurally, they demonstrate awareness of alternative perspectives.
Counterarguments may appear in separate paragraphs or be integrated within body sections, depending on assignment expectations.
Regardless of placement, they must be treated respectfully and accurately.
Responding to Counterarguments Structurally
After presenting a counterargument, the essay must respond to it. This response reinforces the original position rather than ignoring opposing views.
Responses can involve refutation, qualification, or contextualisation of the opposing claim.
This exchange strengthens the argumentative structure by demonstrating critical engagement.
| Section | Purpose | Structural Role |
|---|---|---|
| Main argument paragraph | Advance central claim | Builds persuasive momentum |
| Counterargument paragraph | Acknowledge opposition | Demonstrates critical awareness |
| Response paragraph | Reinforce original position | Restores argumentative control |
This balance enhances academic credibility and logical depth.
Maintaining Coherence Across the Essay
Coherence refers to how smoothly ideas connect throughout the essay. Structurally, this is achieved through consistent argument development and clear transitions.
Each paragraph should clearly relate to the thesis and to surrounding paragraphs. Sudden topic shifts weaken argumentative flow.
Signposting language helps guide readers through complex reasoning.
Common Structural Errors in Argumentative Essays
Frequent structural errors include unclear thesis statements, unrelated body paragraphs, and missing counterarguments.
Another common issue is repetition without development, where the same idea is restated rather than expanded.
These problems often arise from insufficient planning.
Adapting Structure to Disciplinary Contexts
While the general structure remains consistent, disciplinary norms influence emphasis. Scientific arguments may prioritise evidence presentation, while humanities essays may foreground theoretical reasoning.
Students should always review assignment guidelines to align structure with disciplinary expectations.
Flexibility within structure is a sign of academic maturity.
Revising Essay Structure During Editing
Structural revision is a critical stage of the writing process. Students should assess whether each section contributes meaningfully to the argument.
Reordering paragraphs, refining topic sentences, and strengthening transitions often improve clarity.
Structural revision focuses on logic rather than grammar alone.
Why Argumentative Essay Structure Determines Grades
Markers assess structure because it reflects analytical ability. A well-structured essay demonstrates control over ideas and academic conventions.
Even strong research cannot compensate for weak organisation.
Structure allows the argument to be evaluated fairly and systematically.
Final Guidance on Mastering Argumentative Essay Structure
Effective argumentative essay structure is deliberate, logical, and reader-focused. It ensures that arguments unfold clearly and persuasively.
By understanding the function of each section and how ideas should progress, students can present arguments that meet university standards.
Consistent practice and structural awareness are essential for long-term academic success.


Comments