Argumentative and persuasive essays are two of the most common academic writing tasks assigned at college and university level. Because both involve presenting a position and supporting it, students often assume they are interchangeable.
In practice, however, argumentative vs persuasive essays differ in purpose, reasoning style, and examiner expectations. Confusing the two can lead to misplaced emphasis, inappropriate tone, and lower marks—even when the topic knowledge is strong.
This article explains the difference between argumentative and persuasive essays in academic contexts, helping students choose the correct approach and meet assessment criteria with confidence.
Why Students Confuse Argumentative and Persuasive Essays
The confusion between argumentative and persuasive essays arises because both require a clear position on an issue. In everyday language, “argue” and “persuade” are often used interchangeably.
In academic writing, however, these terms describe different intellectual goals. Argumentative essays prioritise reasoned evaluation, while persuasive essays focus on convincing the reader to adopt a viewpoint.
Understanding this distinction is essential for aligning your writing with academic expectations.
Core Purpose of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay aims to evaluate an issue through balanced, evidence-based reasoning. Its primary goal is not to convince emotionally, but to demonstrate critical thinking.
Students are expected to examine multiple perspectives, assess the strength of evidence, and justify a conclusion based on logic rather than preference.
Argumentative essays therefore emphasise fairness, depth, and analytical rigour.
Academic definition: An argumentative essay presents a reasoned position based on critical evaluation of evidence and competing viewpoints.
Core Purpose of a Persuasive Essay
A persuasive essay seeks to influence the reader’s beliefs, attitudes, or actions. While it still relies on evidence, its primary focus is advocacy.
The writer adopts a clear stance early and structures the essay to reinforce that position consistently.
Persuasive essays are more common in applied, reflective, or policy-oriented assignments.
Academic definition: A persuasive essay aims to convince the reader to accept a particular viewpoint or course of action.
Differences in Tone and Voice
Tone is one of the clearest distinctions in the debate of argumentative vs persuasive essays. Argumentative essays use a measured, neutral academic voice.
Persuasive essays may adopt a more assertive tone, directly addressing the reader and emphasising urgency or importance.
Using an overly emotional tone in an argumentative essay often weakens academic credibility.
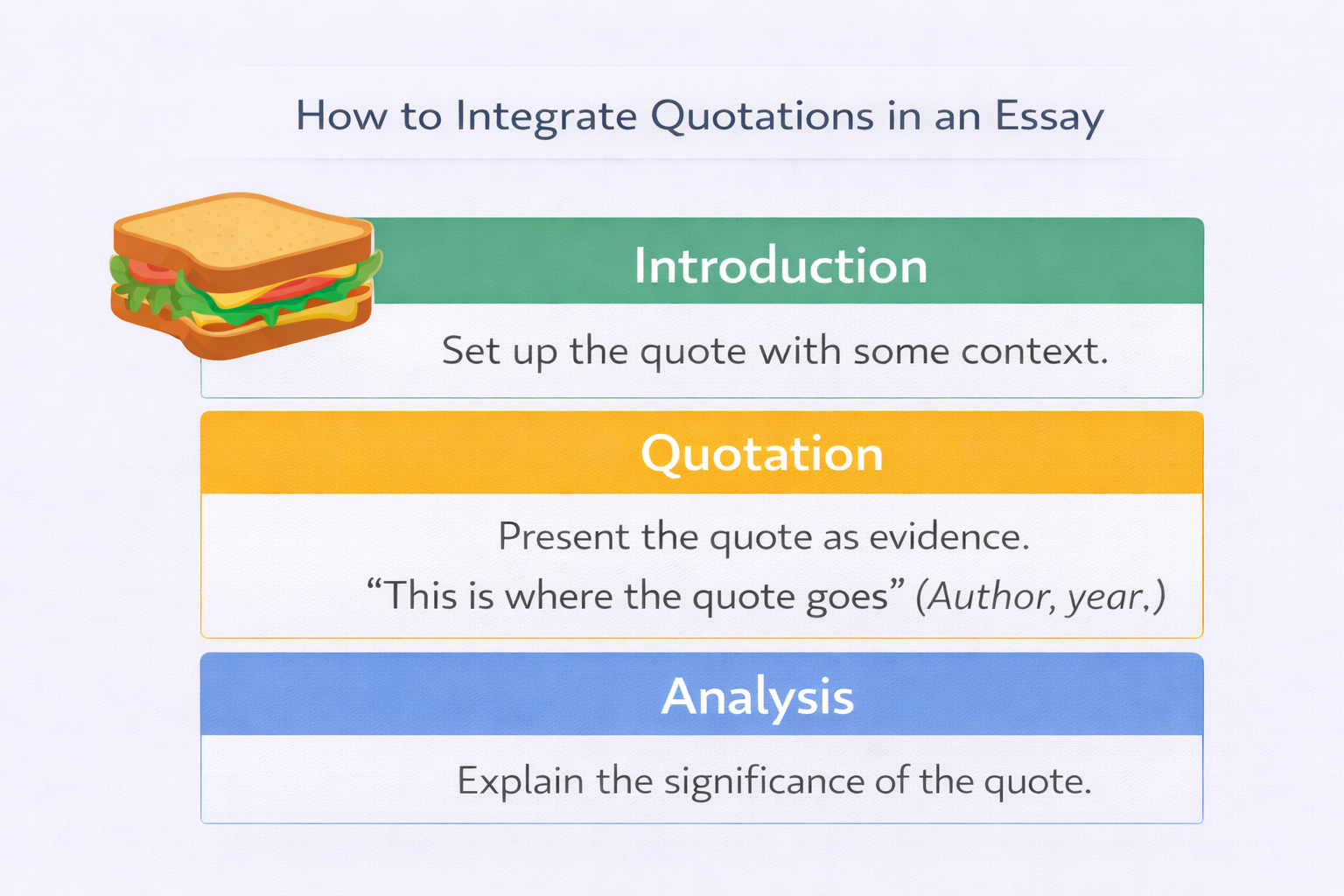
Use of Evidence in Argumentative Essays
Evidence in argumentative essays is used to explore complexity. Sources are evaluated, compared, and sometimes challenged.
Writers are expected to explain limitations, contradictions, and contextual factors affecting evidence.
This balanced use of evidence demonstrates intellectual maturity.
Use of Evidence in Persuasive Essays
In persuasive essays, evidence is selected strategically to support the chosen stance. Counterevidence may be acknowledged but is often minimised.
The emphasis is on reinforcing the central claim rather than exploring uncertainty.
This approach is acceptable when the assignment explicitly calls for persuasion.
Role of Counterarguments
Counterarguments are essential in argumentative essays. Engaging with opposing viewpoints shows analytical depth.
Persuasive essays may include counterarguments, but primarily to refute them and strengthen the writer’s position.
The difference lies in whether counterarguments are examined fairly or strategically dismissed.
| Aspect | Argumentative Essay | Persuasive Essay |
|---|---|---|
| Main purpose | Evaluate and reason | Convince the reader |
| Tone | Neutral and analytical | Assertive and advocative |
| Counterarguments | Explored critically | Refuted strategically |
| Conclusion | Reasoned judgement | Call to belief or action |
The table highlights how the two essay types differ despite surface similarities.
Structural Differences in Practice
Argumentative essays often follow a structure that builds gradually, moving from context to analysis before reaching a conclusion.
Persuasive essays typically introduce the position early and organise paragraphs to reinforce that stance.
Choosing the wrong structure can confuse readers and examiners alike.
Introductions Compared
Argumentative introductions frame the issue broadly and signal a balanced investigation.
Persuasive introductions are more direct, often emphasising urgency or importance.
Recognising this difference helps students set the correct expectations from the outset.
Body Paragraph Development
In argumentative essays, each body paragraph often represents a distinct line of reasoning or perspective.
In persuasive essays, paragraphs are aligned tightly with the central claim, reinforcing it from different angles.
Paragraph focus reflects the essay’s overall purpose.
Conclusions and Final Emphasis
Argumentative conclusions synthesise findings and justify a reasoned position.
Persuasive conclusions aim to leave a strong impression, encouraging acceptance or action.
Confusing these goals can lead to conclusions that feel either weak or inappropriate.
Assessment Criteria and Examiner Expectations
Examiners assess argumentative essays for balance, logic, and critical engagement.
Persuasive essays are judged on clarity of stance, effectiveness of persuasion, and coherence.
Misinterpreting the essay type often results in feedback such as “too opinionated” or “insufficiently analytical.”
Examiner warning: Writing persuasively when an argumentative approach is required can significantly reduce marks.
When to Use Each Essay Type
Argumentative essays are common in disciplines that value evaluation, such as social sciences and humanities.
Persuasive essays are often used in professional, policy, or applied contexts.
Always clarify the task instructions before choosing your approach.
Making the Right Choice in Your Assignment
Before writing, identify whether the task asks you to analyse or to convince.
Key instruction words such as “evaluate,” “discuss,” or “critically analyse” usually signal an argumentative essay.
Words like “argue for,” “advocate,” or “persuade” indicate a persuasive approach.
Final Guidance on Argumentative vs Persuasive Essays
Understanding the difference between argumentative vs persuasive essays is a foundational academic skill.
Each serves a legitimate purpose, but they are not interchangeable in academic assessment.
By matching your reasoning style, tone, and structure to the required essay type, you demonstrate academic awareness and improve your chances of achieving higher grades.


Comments